For older adults who may take multiple prescriptions, safe medication practices are essential for their safety and well being. Your loved one may take medications to help manage chronic conditions, improve comfort, and/or prevent complications. Making sure the right medication and dose is taken at the right times isn’t just a daily task — it’s a crucial part of maintaining health and independence.
The Importance of Safe Medication Management
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 350,000 people are hospitalized each year due to medication-related problems. Older adults are at higher risk because of changes in metabolism, increased sensitivity to drugs, and the potential for multiple prescriptions to interact with one another. While medications help people live longer and healthier lives, they also bring important responsibilities — especially for family caregivers.
What is the Process of Giving Medications to an Older Adult from a Family Caregiver?
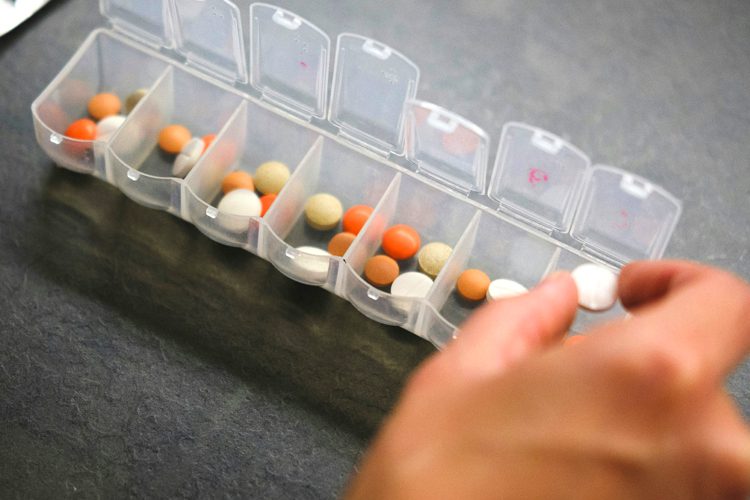
Family caregivers often find themselves stepping into a medical support role, including ensuring safe medication practices. The process of managing and giving medications can vary, but it generally includes:
- Organizing medications: Keeping an up-to-date list of all prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements. Using a pill organizer or a labeled box can help prevent missed or double doses.
- Following the doctor’s orders: Only give medications as prescribed — never change timing, dosage, or frequency without consulting a healthcare provider.
- Documenting doses: A medication log or chart helps track when medications are taken and by whom, reducing the risk of confusion.
- Monitoring for side effects: Noticing changes in mood, alertness, or physical symptoms can help catch adverse reactions early.
- Proper storage: Medications should be kept in a cool, dry place and out of reach of others who might misuse them.
What Are the Risks of Improper Medication Management for Seniors?
When considering Safe medication practices for your loved one, it can be helpful to be aware of some common medication risks:
- Missed or doubled doses: Forgetting to give a medication or giving it twice can cause serious side effects or reduce its effectiveness.
- Drug interactions: Mixing prescriptions, over-the-counter medications, or supplements can lead to dangerous combinations.
- Expired or mislabeled medication: Old or poorly labeled bottles increase the risk of confusion.
- Incorrect administration: Some medications must be taken with food, on an empty stomach, or at specific times — misunderstanding these directions can change how well the medication works.
Because these risks can have real health consequences, it’s vital that caregivers understand their role and limits when it comes to medication administration and seek professional assistance when needed.
Can a Caregiver Administer Medications to an Older Loved One?
In most home settings, as part of safe medication practices, family caregivers can assist with medication reminders — such as handing a loved one their pills or helping set up a weekly pillbox. However, there may be limits to what non-medical caregivers can legally do.
For example, family members without medical training should not administer injections, change dosages, or give crushed or altered medications unless directed by a healthcare professional. These actions could require the supervision or direct administration of a Registered Nurse (RN) or licensed professional.
If you’re unsure what’s allowed, talk with your loved one’s doctor, pharmacist, or a local senior care expert. They can help you understand your responsibilities and connect you with in-home nursing or medication management support if needed.
What Medication Safety Guidelines Should Family Caregivers Follow?

To promote safety and peace of mind, follow these key guidelines:
- Keep an updated medication list with doses, schedules, and prescribing physicians.
- Use one pharmacy whenever possible so the pharmacist can check for interactions.
- Set alarms or reminders to stay on schedule.
- Review medications regularly with a healthcare provider to ensure each one is still necessary.
- Never share prescriptions or give medications prescribed for someone else.
- Ask questions. Pharmacists and nurses are valuable resources for learning about side effects, storage, and administration tips.
When Should a Registered Nurse (RN) Be Involved in Administering Medications for Seniors?

Certain situations require the expertise of a licensed nurse. A Registered Nurse may be needed when:
- The medication must be injected or delivered through a medical device (like an insulin pen or IV).
- The person has trouble swallowing pills or needs medications crushed or mixed in food.
- There are complex medication regimens involving multiple daily doses or high-risk drugs such as anticoagulants or pain management prescriptions
- The senior is showing signs of adverse reactions that need professional assessment.
In assisted living communities like Dayspring Villa, staff receive specialized training and certification (QMAP) to ensure that residents receive medications safely, accurately, and on time. This support can bring significant peace of mind to families.
When Is Assisted Living the Right Choice for Medication Support?
If you’re feeling overwhelmed by providing safe medication practices, or if your loved one requires more complex medication management than you feel comfortable providing, assisted living can be an excellent solution.
At Dayspring Villa Senior Living Community, residents benefit from:
- Certified staff overseeing medication administration.
- Regular health monitoring and communication with physicians.
- A safe, supportive environment where residents receive the care they need while maintaining independence.
Medication management can become a big part of daily life as we age. While it can be stressful, with the right support — whether through careful family caregiving or professional assisted living services — seniors can stay healthy, safe, and well cared for.